- Scikit Image – Introduction
- Scikit Image - Image Processing
- Scikit Image - Numpy Images
- Scikit Image - Image datatypes
- Scikit Image - Using Plugins
- Scikit Image - Image Handlings
- Scikit Image - Reading Images
- Scikit Image - Writing Images
- Scikit Image - Displaying Images
- Scikit Image - Image Collections
- Scikit Image - Image Stack
- Scikit Image - Multi Image
- Scikit Image - Data Visualization
- Scikit Image - Using Matplotlib
- Scikit Image - Using Ploty
- Scikit Image - Using Mayavi
- Scikit Image - Using Napari
- Scikit Image - Color Manipulation
- Scikit Image - Alpha Channel
- Scikit Image - Conversion b/w Color & Gray Values
- Scikit Image - Conversion b/w RGB & HSV
- Scikit Image - Conversion to CIE-LAB Color Space
- Scikit Image - Conversion from CIE-LAB Color Space
- Scikit Image - Conversion to luv Color Space
- Scikit Image - Conversion from luv Color Space
- Scikit Image - Image Inversion
- Scikit Image - Painting Images with Labels
- Scikit Image - Contrast & Exposure
- Scikit Image - Contrast
- Scikit Image - Contrast enhancement
- Scikit Image - Exposure
- Scikit Image - Histogram Matching
- Scikit Image - Histogram Equalization
- Scikit Image - Local Histogram Equalization
- Scikit Image - Tinting gray-scale images
- Scikit Image - Image Transformation
- Scikit Image - Scaling an image
- Scikit Image - Rotating an Image
- Scikit Image - Warping an Image
- Scikit Image - Affine Transform
- Scikit Image - Piecewise Affine Transform
- Scikit Image - ProjectiveTransform
- Scikit Image - EuclideanTransform
- Scikit Image - Radon Transform
- Scikit Image - Line Hough Transform
- Scikit Image - Probabilistic Hough Transform
- Scikit Image - Circular Hough Transforms
- Scikit Image - Elliptical Hough Transforms
- Scikit Image - Polynomial Transform
- Scikit Image - Image Pyramids
- Scikit Image - Pyramid Gaussian Transform
- Scikit Image - Pyramid Laplacian Transform
- Scikit Image - Swirl Transform
- Scikit Image - Morphological Operations
- Scikit Image - Erosion
- Scikit Image - Dilation
- Scikit Image - Black & White Tophat Morphologies
- Scikit Image - Convex Hull
- Scikit Image - Generating footprints
- Scikit Image - Isotopic Dilation & Erosion
- Scikit Image - Isotopic Closing & Opening of an Image
- Scikit Image - Skelitonizing an Image
- Scikit Image - Morphological Thinning
- Scikit Image - Masking an image
- Scikit Image - Area Closing & Opening of an Image
- Scikit Image - Diameter Closing & Opening of an Image
- Scikit Image - Morphological reconstruction of an Image
- Scikit Image - Finding local Maxima
- Scikit Image - Finding local Minima
- Scikit Image - Removing Small Holes from an Image
- Scikit Image - Removing Small Objects from an Image
- Scikit Image - Filters
- Scikit Image - Image Filters
- Scikit Image - Median Filter
- Scikit Image - Mean Filters
- Scikit Image - Morphological gray-level Filters
- Scikit Image - Gabor Filter
- Scikit Image - Gaussian Filter
- Scikit Image - Butterworth Filter
- Scikit Image - Frangi Filter
- Scikit Image - Hessian Filter
- Scikit Image - Meijering Neuriteness Filter
- Scikit Image - Sato Filter
- Scikit Image - Sobel Filter
- Scikit Image - Farid Filter
- Scikit Image - Scharr Filter
- Scikit Image - Unsharp Mask Filter
- Scikit Image - Roberts Cross Operator
- Scikit Image - Lapalace Operator
- Scikit Image - Window Functions With Images
- Scikit Image - Thresholding
- Scikit Image - Applying Threshold
- Scikit Image - Otsu Thresholding
- Scikit Image - Local thresholding
- Scikit Image - Hysteresis Thresholding
- Scikit Image - Li thresholding
- Scikit Image - Multi-Otsu Thresholding
- Scikit Image - Niblack and Sauvola Thresholding
- Scikit Image - Restoring Images
- Scikit Image - Rolling-ball Algorithm
- Scikit Image - Denoising an Image
- Scikit Image - Wavelet Denoising
- Scikit Image - Non-local means denoising for preserving textures
- Scikit Image - Calibrating Denoisers Using J-Invariance
- Scikit Image - Total Variation Denoising
- Scikit Image - Shift-invariant wavelet denoising
- Scikit Image - Image Deconvolution
- Scikit Image - Richardson-Lucy Deconvolution
- Scikit Image - Recover the original from a wrapped phase image
- Scikit Image - Image Inpainting
- Scikit Image - Registering Images
- Scikit Image - Image Registration
- Scikit Image - Masked Normalized Cross-Correlation
- Scikit Image - Registration using optical flow
- Scikit Image - Assemble images with simple image stitching
- Scikit Image - Registration using Polar and Log-Polar
- Scikit Image - Feature Detection
- Scikit Image - Dense DAISY Feature Description
- Scikit Image - Histogram of Oriented Gradients
- Scikit Image - Template Matching
- Scikit Image - CENSURE Feature Detector
- Scikit Image - BRIEF Binary Descriptor
- Scikit Image - SIFT Feature Detector and Descriptor Extractor
- Scikit Image - GLCM Texture Features
- Scikit Image - Shape Index
- Scikit Image - Sliding Window Histogram
- Scikit Image - Finding Contour
- Scikit Image - Texture Classification Using Local Binary Pattern
- Scikit Image - Texture Classification Using Multi-Block Local Binary Pattern
- Scikit Image - Active Contour Model
- Scikit Image - Canny Edge Detection
- Scikit Image - Marching Cubes
- Scikit Image - Foerstner Corner Detection
- Scikit Image - Harris Corner Detection
- Scikit Image - Extracting FAST Corners
- Scikit Image - Shi-Tomasi Corner Detection
- Scikit Image - Haar Like Feature Detection
- Scikit Image - Haar Feature detection of coordinates
- Scikit Image - Hessian matrix
- Scikit Image - ORB feature Detection
- Scikit Image - Additional Concepts
- Scikit Image - Render text onto an image
- Scikit Image - Face detection using a cascade classifier
- Scikit Image - Face classification using Haar-like feature descriptor
- Scikit Image - Visual image comparison
- Scikit Image - Exploring Region Properties With Pandas
Scikit Image - Denoising an Image
Denoising an image refers to the process of reducing or removing noise from a digital image. Noise in an image typically appears as random variations in brightness or color that are not part of the original scene or subject being photographed. The goal of image denoising is to enhance the quality of an image by eliminating or reducing these unwanted and distracting artifacts, making the image cleaner, and more visually appealing.
The Scikit Image library offers a range of denoising filters for image processing, allowing users to remove noise from noisy images and recover the original image. In this tutorial, we will explore three different denoising filters provided by Scikit Image −
Total Variation Filter (skimage.restoration.denoise_tv_chambolle())
The total variation filter aims to minimize the total variation norm of the image while maintaining its similarity to the original. Total variation is essentially the L1 norm of the image's gradient.
Bilateral Filter (skimage.restoration.denoise_bilateral())
The bilateral filter is designed to preserve edges while reducing noise. It considers both spatial proximity and radiometric similarity when averaging pixel values.
Wavelet Denoising Filter (skimage.restoration.denoise_wavelet())
This filter relies on the wavelet representation of the image. It identifies noise as small values in the wavelet domain and sets them to zero. This filter is especially effective at reducing noise while preserving image details.
In color images, wavelet denoising is often performed in the YCbCr color space to avoid introducing more noticeable noise in individual color channels.
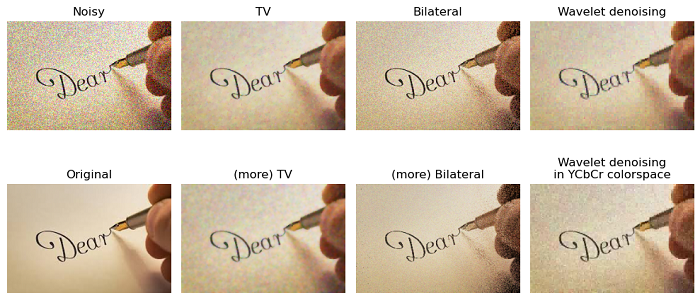
To illustrate the effectiveness of these denoising filters(total variation, bilateral, and wavelet denoising), we'll apply them to a noisy image.
Example
The following example demonstrates the application of total variation, bilateral, and wavelet denoising filters on a noisy image.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.restoration import (denoise_tv_chambolle, denoise_bilateral, denoise_wavelet, estimate_sigma)
from skimage import io, img_as_float
from skimage.util import random_noise
# Load an input image
original = img_as_float(io.imread('Images/hand writting.jpg'))
# Add Gaussian noise to create a noisy version of the image.
sigma = 0.155
noisy = random_noise(original, var=sigma**2)
# Estimate the average noise standard deviation across color channels.
sigma_est = estimate_sigma(noisy, channel_axis=-1, average_sigmas=True)
print(f'Estimated Gaussian noise standard deviation = {sigma_est}')
# Create a figure with a 2x4 grid for displaying images.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=4, figsize=(10,5), sharex=True, sharey=True)
ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4, ax5, ax6, ax7 = axes.ravel()
plt.gray()
# Display the noisy image.
ax0.imshow(noisy)
ax0.set_title('Noisy')
# Apply Total Variation (TV) denoising with a specified weight
ax1.imshow(denoise_tv_chambolle(noisy, weight=0.1, channel_axis=-1))
ax1.set_title('TV')
# Apply Bilateral denoising with specified sigma parameters.
ax2.imshow(denoise_bilateral(noisy, sigma_color=0.05, sigma_spatial=15, channel_axis=-1))
ax2.set_title('Bilateral')
# Apply Wavelet denoising.
ax3.imshow(denoise_wavelet(noisy, channel_axis=-1, rescale_sigma=True))
ax3.set_title('Wavelet denoising')
# Display the original image
ax4.imshow(original)
ax4.set_title('Original')
# Apply TV denoising with a different weight.
ax5.imshow(denoise_tv_chambolle(noisy, weight=0.2, channel_axis=-1))
ax5.set_title('(more) TV')
# Apply Bilateral denoising with different sigma parameters.
ax6.imshow(denoise_bilateral(noisy, sigma_color=0.1, sigma_spatial=15, channel_axis=-1))
ax6.set_title('(more) Bilateral')
# Apply Wavelet denoising in the YCbCr colorspace.
ax7.imshow(denoise_wavelet(noisy, channel_axis=-1, convert2ycbcr=True, rescale_sigma=True))
ax7.set_title('Wavelet denoising\nin YCbCr colorspace')
for ax in axes.flat:
ax.axis('off')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output
Estimated Gaussian noise standard deviation = 0.1415983008453029