- SciPy - Home
- SciPy - Introduction
- SciPy - Environment Setup
- SciPy - Basic Functionality
- SciPy - Relationship with NumPy
- SciPy Clusters
- SciPy - Clusters
- SciPy - Hierarchical Clustering
- SciPy - K-means Clustering
- SciPy - Distance Metrics
- SciPy Constants
- SciPy - Constants
- SciPy - Mathematical Constants
- SciPy - Physical Constants
- SciPy - Unit Conversion
- SciPy - Astronomical Constants
- SciPy - Fourier Transforms
- SciPy - FFTpack
- SciPy - Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
- SciPy - Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)
- SciPy Integration Equations
- SciPy - Integrate Module
- SciPy - Single Integration
- SciPy - Double Integration
- SciPy - Triple Integration
- SciPy - Multiple Integration
- SciPy Differential Equations
- SciPy - Differential Equations
- SciPy - Integration of Stochastic Differential Equations
- SciPy - Integration of Ordinary Differential Equations
- SciPy - Discontinuous Functions
- SciPy - Oscillatory Functions
- SciPy - Partial Differential Equations
- SciPy Interpolation
- SciPy - Interpolate
- SciPy - Linear 1-D Interpolation
- SciPy - Polynomial 1-D Interpolation
- SciPy - Spline 1-D Interpolation
- SciPy - Grid Data Multi-Dimensional Interpolation
- SciPy - RBF Multi-Dimensional Interpolation
- SciPy - Polynomial & Spline Interpolation
- SciPy Curve Fitting
- SciPy - Curve Fitting
- SciPy - Linear Curve Fitting
- SciPy - Non-Linear Curve Fitting
- SciPy - Input & Output
- SciPy - Input & Output
- SciPy - Reading & Writing Files
- SciPy - Working with Different File Formats
- SciPy - Efficient Data Storage with HDF5
- SciPy - Data Serialization
- SciPy Linear Algebra
- SciPy - Linalg
- SciPy - Matrix Creation & Basic Operations
- SciPy - Matrix LU Decomposition
- SciPy - Matrix QU Decomposition
- SciPy - Singular Value Decomposition
- SciPy - Cholesky Decomposition
- SciPy - Solving Linear Systems
- SciPy - Eigenvalues & Eigenvectors
- SciPy Image Processing
- SciPy - Ndimage
- SciPy - Reading & Writing Images
- SciPy - Image Transformation
- SciPy - Filtering & Edge Detection
- SciPy - Top Hat Filters
- SciPy - Morphological Filters
- SciPy - Low Pass Filters
- SciPy - High Pass Filters
- SciPy - Bilateral Filter
- SciPy - Median Filter
- SciPy - Non - Linear Filters in Image Processing
- SciPy - High Boost Filter
- SciPy - Laplacian Filter
- SciPy - Morphological Operations
- SciPy - Image Segmentation
- SciPy - Thresholding in Image Segmentation
- SciPy - Region-Based Segmentation
- SciPy - Connected Component Labeling
- SciPy Optimize
- SciPy - Optimize
- SciPy - Special Matrices & Functions
- SciPy - Unconstrained Optimization
- SciPy - Constrained Optimization
- SciPy - Matrix Norms
- SciPy - Sparse Matrix
- SciPy - Frobenius Norm
- SciPy - Spectral Norm
- SciPy Condition Numbers
- SciPy - Condition Numbers
- SciPy - Linear Least Squares
- SciPy - Non-Linear Least Squares
- SciPy - Finding Roots of Scalar Functions
- SciPy - Finding Roots of Multivariate Functions
- SciPy - Signal Processing
- SciPy - Signal Filtering & Smoothing
- SciPy - Short-Time Fourier Transform
- SciPy - Wavelet Transform
- SciPy - Continuous Wavelet Transform
- SciPy - Discrete Wavelet Transform
- SciPy - Wavelet Packet Transform
- SciPy - Multi-Resolution Analysis
- SciPy - Stationary Wavelet Transform
- SciPy - Statistical Functions
- SciPy - Stats
- SciPy - Descriptive Statistics
- SciPy - Continuous Probability Distributions
- SciPy - Discrete Probability Distributions
- SciPy - Statistical Tests & Inference
- SciPy - Generating Random Samples
- SciPy - Kaplan-Meier Estimator Survival Analysis
- SciPy - Cox Proportional Hazards Model Survival Analysis
- SciPy Spatial Data
- SciPy - Spatial
- SciPy - Special Functions
- SciPy - Special Package
- SciPy Advanced Topics
- SciPy - CSGraph
- SciPy - ODR
- SciPy Useful Resources
- SciPy - Reference
- SciPy - Quick Guide
- SciPy - Cheatsheet
- SciPy - Useful Resources
- SciPy - Discussion
SciPy - interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() Function
scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() is a function in SciPy which is used to perform polynomial interpolation using the Barycentric Lagrange method. It constructs an interpolating polynomial that passes through a set of given points (xi, yi).
This method is numerically stable and efficient for high-degree polynomials by avoiding common issues like Runge's phenomenon. This function evaluates the interpolated polynomial at specified points.
Syntax
Following is the syntax of the function scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() to perform polynomial interpolation −
scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x, axis=0, *, der=0)
Parameters
Here are the parameters of the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function −
- xi(array-like): 1-D array of data points where interpolation is performed i.e., the x-coordinates of the known data points.
- yi(array-like): 1-D array of values corresponding to the data points i.e., the y-coordinates of the known data points.
- x(array-like): Points at which to evaluate the interpolated values i.e., the x-coordinates where we want the output.
- axis(int, optional): The axis along which to interpolate. For 1-D input this parameter is typically set to 0.
- der(int, optional): If der is set to default value 0 then the function returns the interpolated values. If der is 1 then it returns the first derivative and so on.
Return Value
The scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function returns the interpolated values at the specified points x. If der is greater than 0 then it returns the derivatives of the interpolating polynomial at those points.
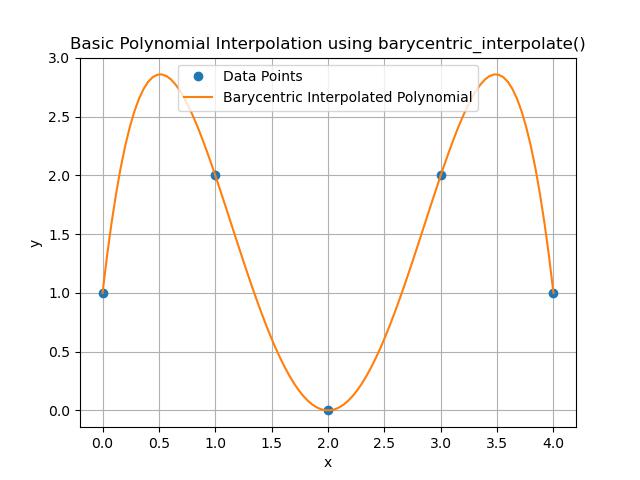
Basic Polynomial Interpolation
Following is the example of using the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function which is used to perform polynomial interpolation −
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import barycentric_interpolate
# Define data points
xi = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) # x-values
yi = np.array([1, 2, 0, 2, 1]) # y-values
# Create new x points for interpolation
x_new = np.linspace(0, 4, 100) # 100 points between 0 and 4
# Perform barycentric interpolation
y_new = barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x_new)
# Plot original data points and the interpolated polynomial
plt.plot(xi, yi, 'o', label='Data Points') # Original points
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, label='Barycentric Interpolated Polynomial') # Interpolated curve
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Basic Polynomial Interpolation using barycentric_interpolate()')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Here is the output of the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function −
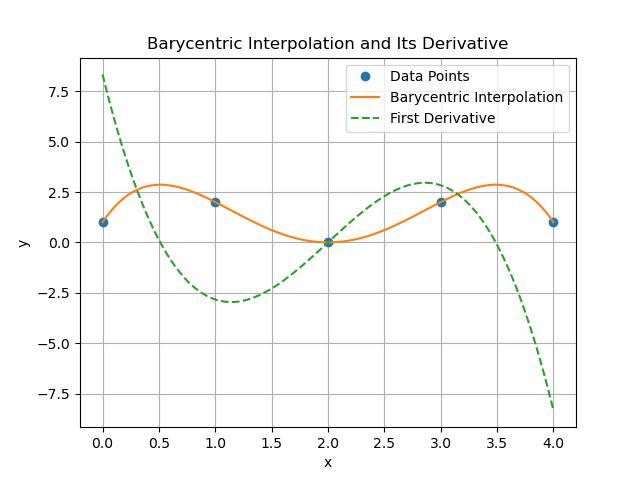
Evaluating Derivatives
This example effectively shows how to evaluate the derivatives of a polynomial that has been interpolated using the Barycentric method. The derivative plot shows the rate of change of the polynomial across the range defined by the data points −
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import barycentric_interpolate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define data points
xi = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
yi = np.array([1, 2, 0, 2, 1])
# Points to evaluate the interpolation
x_new = np.linspace(0, 4, 100) # 100 points between 0 and 4
# Perform interpolation
y_new = barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x_new)
# Calculate first derivative
y_deriv = barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x_new, der=1)
# Plot original points, the interpolated polynomial, and its derivative
plt.plot(xi, yi, 'o', label='Data Points') # Original points
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, label='Barycentric Interpolation') # Interpolated curve
plt.plot(x_new, y_deriv, label='First Derivative', linestyle='--') # Derivative curve
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Barycentric Interpolation and Its Derivative')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Here is the output of the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function which is used to evaluate the Derivatives −
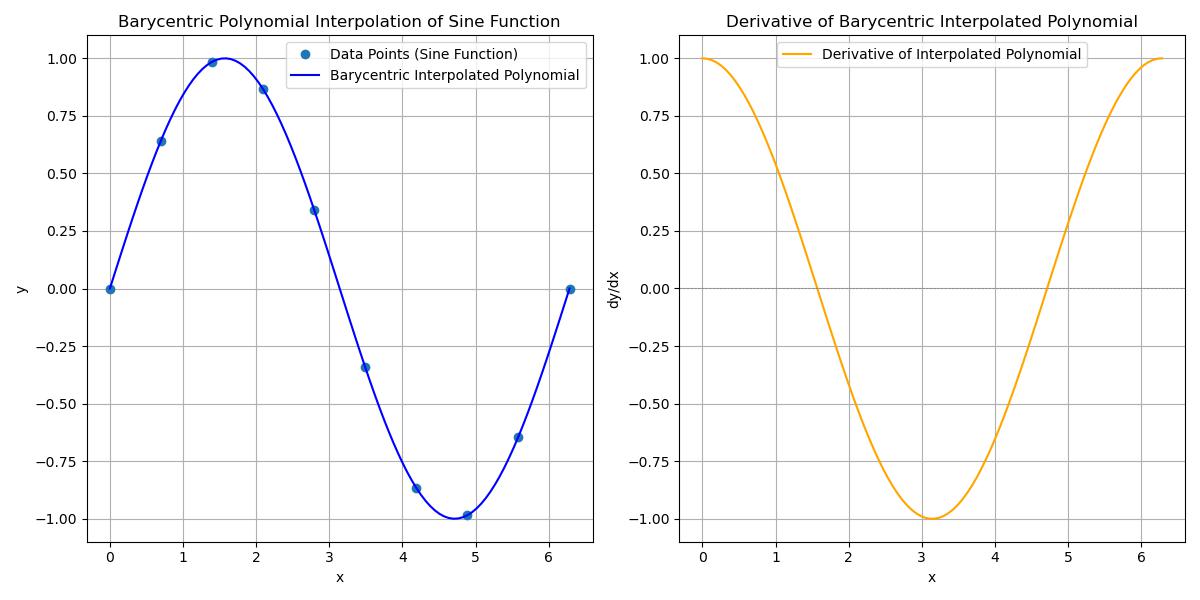
Using More Complex Data Points
Here is an example of the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function which uses the more complex data points −
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.interpolate import barycentric_interpolate
# Define complex data points based on a sine function
xi = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 10) # 10 x-values from 0 to 2p
yi = np.sin(xi) # Corresponding y-values using the sine function
# Create new x points for interpolation
x_new = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100) # 100 points between 0 and 2p
# Perform barycentric interpolation
y_new = barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x_new)
# Define a function to compute the derivative using finite differences
def derivative(xi, yi, x, h=1e-5):
return (barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x + h) - barycentric_interpolate(xi, yi, x - h)) / (2 * h)
# Compute the derivatives at the new x points
y_derivative = derivative(xi, yi, x_new)
# Plot original data points, interpolated polynomial, and its derivative
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
# Subplot for the interpolated polynomial
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(xi, yi, 'o', label='Data Points (Sine Function)') # Original points
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, label='Barycentric Interpolated Polynomial', color='blue') # Interpolated curve
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Barycentric Polynomial Interpolation of Sine Function')
plt.grid()
# Subplot for the derivative
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(x_new, y_derivative, label='Derivative of Interpolated Polynomial', color='orange')
plt.axhline(0, color='grey', lw=0.5, ls='--') # Horizontal line at y=0
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('dy/dx')
plt.title('Derivative of Barycentric Interpolated Polynomial')
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Here is the output of the scipy.interpolate.barycentric_interpolate() function using the complex data points −